Contributed by Bray, Inc.
Kele is thrilled to announce a new partnership with Bray that is helping us kick off 2024 with a bang! Their catalog offering is deep and so is their knowledge, which is why Kele now offers over 27k Bray products that we know you’ll love.
Here’s just one example of how knowledgeable and industry-focused they are. Happy learning!
(foreword by Kele)
SAFETY INSTRUMENTED SYSTEM VALVES (SIS) & AUTOMATED EMERGENCY BLOCK VALVES (EBV)
Safety Instrumented System Valves or EBV’s are used to isolate/vent a process stream when unsafe process conditions exist. Actions required can be to open or close based on the process. Due to the critical nature of these valves, frequent testing is needed to ensure proper function during an emergency.
The role of a valve test is to verify the appropriate movement will occur during an event. Since full travel of the valve will interrupt the day-to-day process, a partial stroke test (PST) can be done as an unobtrusive option. This test will ensure all moving components are in working order by stroking the valve a few degrees. The test can be performed in many ways ranging from mechanical to fully automated digital solutions.
Full Stroke Testing (FST) adds the capability of validating the whole stroke of the valve. This test can be done during a plant shutdown since it will interrupt the process.
TEST = OPTIONS ARE:
> Manually Operated Mechanical PST
> Digitally Automated PST
> Digitally Automated FST
FEATURES
Manually Operated PST Provides:
• High degree of assurance that a complete valve movement will occur on demand
• Verification that the valve torque is still below actuator operating torque
• Local visual confirmation
Digitally Automated PST Provides:
• Verification that the control signals are operating as designed
• Customizable alarm sensitivity
• Valve condition evaluation and comparison to original PST signature
• Compliance reporting
Digitally Automated FST Provides:
• 100% confirmation of valve travel and confirmation of valve sealing conformance
• Valve condition evaluation and comparison to original FST signature
• Reduction in human error
DETAILED OPERATION AND CUSTOMIZATION
1. MANUALLY OPERATED MECHANICAL
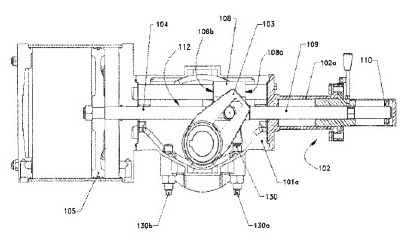
PST S98 PARTIAL STROKE MODULE
The Bray PST module is an all-mechanical device that can be added to the S98 scotch yoke actuator. This patented design can serve as a dual function of extended travel stop and partial stroke test.
HOW IT WORKS
With the hand lever set in free mode, the push rod is free to move through the device allowing a full range of travel. When the hand lever is activated the push rod travel is limited. This travel limit can be adjusted anywhere in the valve rotation profile.

APPLICATION
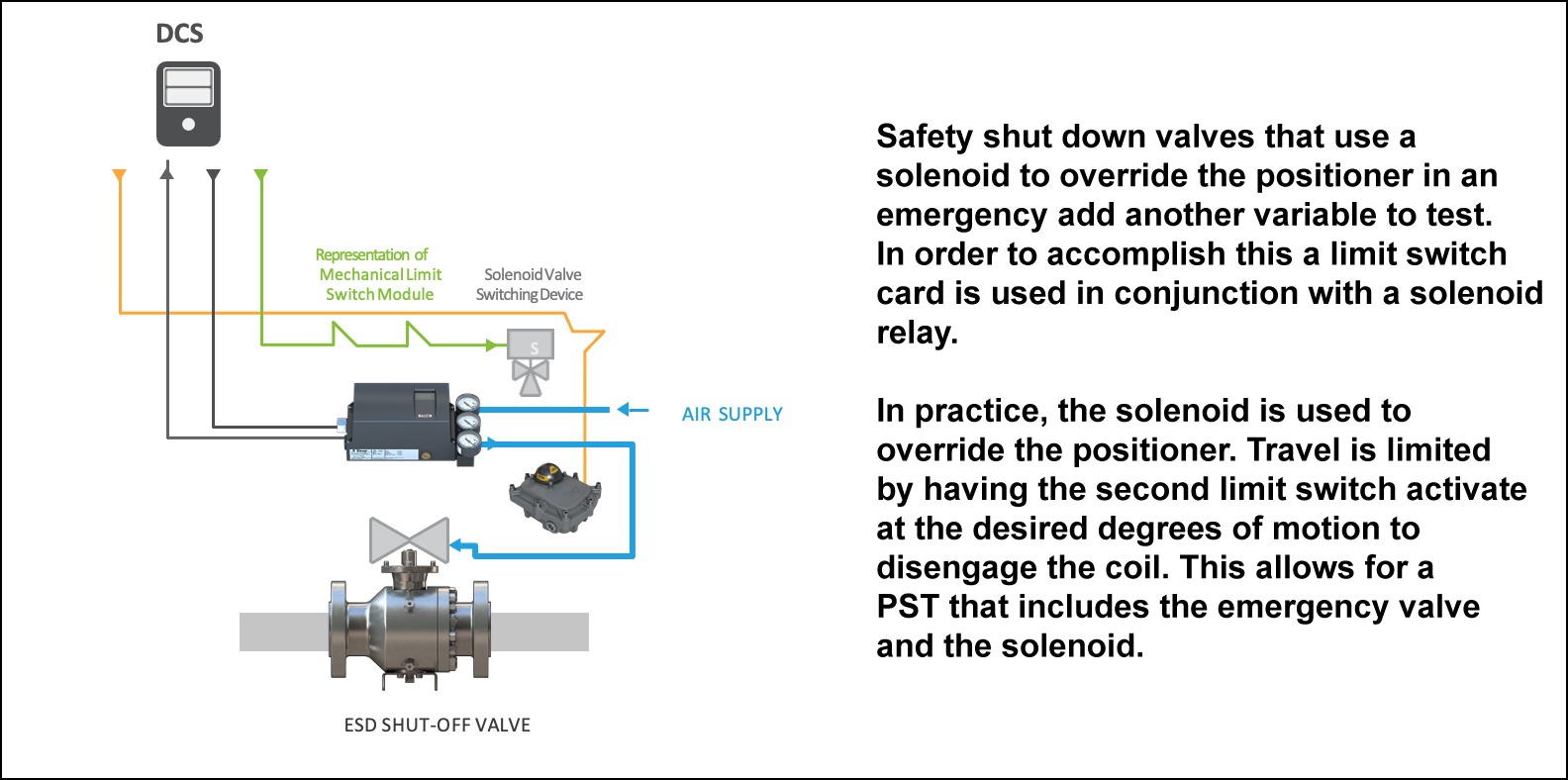
By manually limiting the rotation of the valve to a small degree of movement the solenoid can be used to activate a partial stroke test. This test can be done locally at the unit by a technician without the use of outside electronics.
2. DIGITALLY AUTOMATED PST
ELECTRONIC APPROACHES
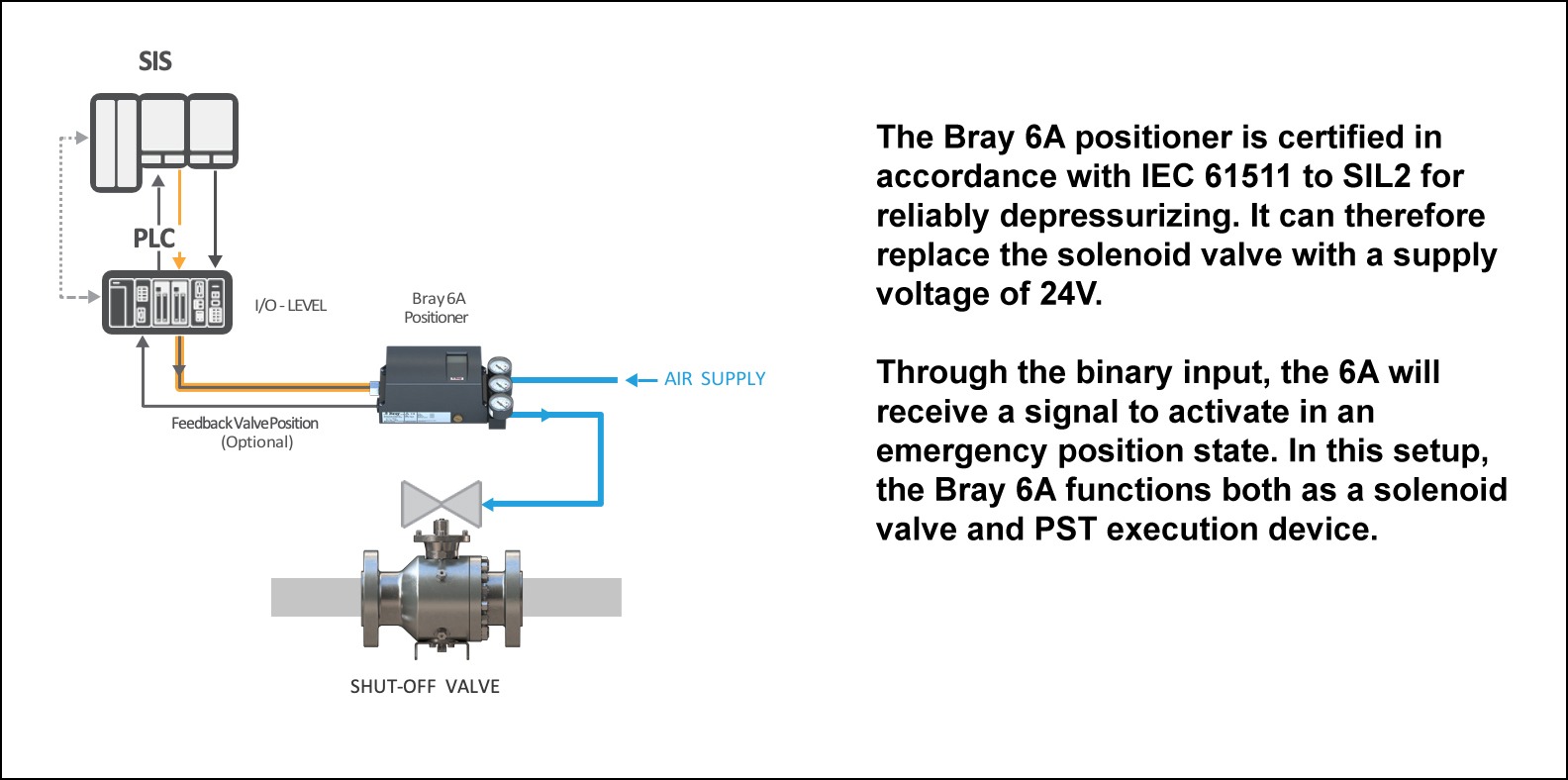
PST can also be done digitally with the use of a smart positioner such as the Bray 6A. By using a digital approach variables such as stiction, speed, dwell time, and friction are measured. These
variables improve the quality of a partial stroke test and help in predicting valve faults earlier than mechanical solutions. This is done by comparing tested values against user/manufacturer-defined limits. A second advantage is in the data logging capabilities of the Bray 6A. By documenting every test, the Bray 6A provides plant managers with a record that all testing processes are being performed in accordance with safety standards.
FULL CONTROLLABILITY
The Bray 6A provides plant managers control over multiple variables in the PST. Variables such as start position, stroke length, and ramp rate can be adjusted to meet the needs of the plant.
INITIATING A TEST CAN BE DONE MULTIPLE WAYS.
1. Local or remote initiation with Binary input activation
The 6A smart positioner is equipped with 1 binary input slot as standard. This input can be used to activate the partial stroke test ether remotely with PLC/DCS or by ESD push button
2. Data management software communicating through HART protocol
Units that are equipped with HART or Profibus will have the capability of activating a PST or FST through software. With the use of asset management software, all Bray 6A positioners in a plant are given a unique ID name chosen by the user. Through this system, plant managers will have the ability to view all positioners and run PST/FST as needed with real-time data being presented in the control room. PST/FST settings can be adjusted for individual positioners or by valve type/size/features/application. Variables such as test frequency, stroke distance, and time can be adjusted to improve performance on the fly.

3. Adjustable Cyclic Test Interval at agreed threshold safe start point
The Bray 6A positioner can be programmed to automatically run a PST at designated time intervals. Activation of this mode can be done both locally to the unit or remotely through the PDM software. Time intervals are done in days allowing users to meet their minimum availability requirements for an automated safe start point.
EXAMPLE 6A CIRCUITS
PST WITH SOLENOID
PST NO SOLENOID
3. DIGITALLY AUTOMATED FST
When possible, a full stroke test can be done to validate a full stroke signature and ensure valve isolation or unseating capability. Like a PST the FST is logged in the Bray 6A memory. An example of a full stroke baseline test response can be seen in the chart below.
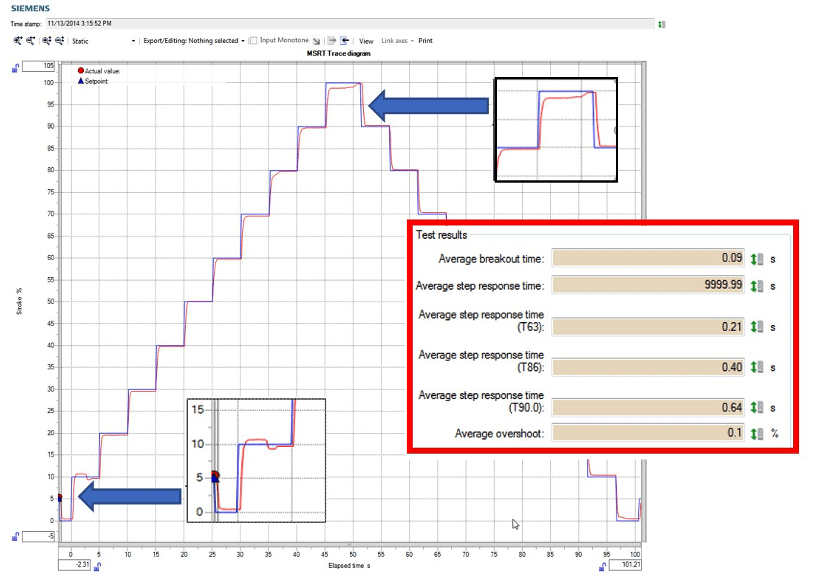
ALARM NOTIFICATIONS
The 6A positioner has the capability of outputting alarm codes based on measured values such as valve torque increase over time, valve movement time, and hours of operation. A 3-tiered scale can be used to indicate the severity of variable changes. The below images outline the visual display of each alarm level found on the Bray 6A screen.
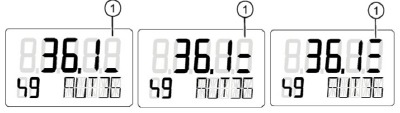
For a networked unit, this alarm can be sent to a PLC or DCS through a protocol network or binary outputs. Further diagnostics can drill down to the specific alarm reason.
As an example, in the context of a PST, the tiered system can be applied to the time required to run the PST. The below table outlines the tired alarm program for a 3-second PST.
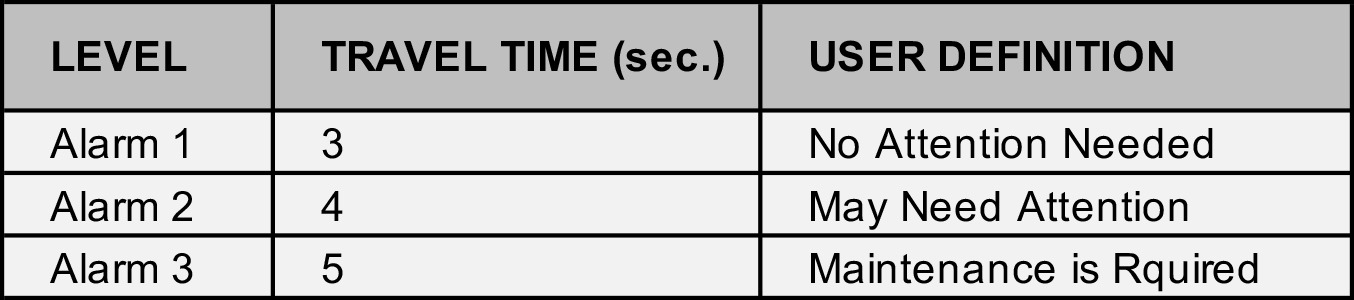
By giving users the ability to control the sensitivity and relevance of these alarm variables you can create a system that reduces false positives and provides the user with fully customized valve reliability testing.
Check out Bray products and solutions now at Kele!




